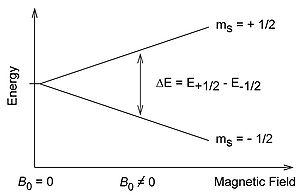
Basic principles Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) = Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy Same underlying physical principles as in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) One unpaired (free) electron: Zeeman effect: ∆𝑈=𝑔 𝑒 𝑔=.
ESR is a spectroscopic technique that detects chemical species that have unpaired electrons:. Transition metal ions and complexes Mn 2+, Cu 2+, Gd 3+ etc. Simple inorganic compounds: O 2, NO 2. Short-lived intermediate radicals OH, H, F etc. In kinetics study Defects in crystals. Electrons trapped in radiation damaged sites Stable organic radicals Triplet states Biological applications: Paramagnetic cofactors: iron sulfur, copper proteins Free radicals of biological origin and their spin-trapping products. Spin-labeling An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007.

Relaxation Evolution of a spin system is described by Bloch equations: Mx’, My’ Mz – magnetization components in the rotating frame 0= e. H 0 – the Larmor Frequency T 1 - spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation time T 2 - spin-spin or traverse relaxation time When properly integrated, the Bloch equations will yield the X', Y', and Z components of magnetization as a function of time. Stationary solution in the rotating frame gives a lorentzian line Gaussian line ESR linewidth: = inhomogeneous broadening k=1 Lorentz Gauss An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. ESR and NMR are very different methods! Electron proton ratio Rest mass me =9. 1094.10 -28 g mp =1. 6726.10 -24 g 5.
446.10 -4 Charge e=-4. 80286.10 -10 ESU e=4. 80286.10 -10 ESU -1 Angular momentum h/4 p 1 Magnetic dipole moment m.
002322 me=eh/4 pmec = 9. 274.10 -21 erg/G g.
0504.10 -24 erg/G 1836. 12 Frequency: Factor 1000 larger in EPR! (GHz instead of MHz) Coupling strength: Factor 1 000 larger in EPR! (MHz instead of Hz) Relaxation Times: Factor 1000 smaller in EPR! (ns instead of ms) = much higher techniqual requirements, but unique sensitivity to molecular motion Sensitivity: Factor 1 000 better than in NMR!! M instead of 1 m. M ) An ideal case, though An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007.
The Basic ESR Experiment (conventional ESR) Unlike NMR a large proportion of machines are still 'cw'. That is they do not use pulsed detection methods. ESR is done from 1 to 300+GHz 30 m. T-10 T or 30 cm-1 mm, up to 2000+ GHz Machines are classified according to their source frequency: Commonly used X-band at 9.
0), Ku (17), K (23), Q (36), V (50), W (95), D(140), G(180). Field modulation is used to encode the spectrum 1 st derivative lineshape. Use microwave transmission lines. Do spectroscopy with a few microwatts to a few milliwatts of power. Solid state Gunn diode or DRO or tube klystron sources. Temperatures from 4 K (heme and non-heme iron) to 310 K+ (in vivo/vitro).
Sensitivity: Increases as (frequency)2, but limited by sample size, field homogeneity and component construction problems. Practically (at X-band): detect 1011 spins, a detectable concentration of 10 -9 M. An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. A - the hyperfine splitting The unpaired electron, which gives us the EPR spectrum, is very sensitive to local fields in its surroundings. Local fields arising from magnetic nuclei are permanent and independent of H. Interaction with neighboring nuclear magnetic dipoles gives the nuclear hyperfine interaction and hyperfine splitting A Corresponds to the NMR coupling constant J A splittings are independent of the external field.
For several equivalent nuclei n, (2 n. MIM + 1) transitions are observed for a nucleus M with a spin I The relative intensities are given by Pascal's triangle for I = ½ 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 5 10 10 5 1 1 6 15 20 15 6 1 1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1 An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. Anisotropy in g and A Many measurements are made in the solid state in EPR spectroscopy. The ability of EPR to obtain useful information from amorphous (glassy) and polycrystalline (powders) as well as from single crystal materials has attracted much biology and biochemistry research Usually: g. Z are not all equal, so g is anisotropic. Same for AX, AY, AZ.
For EPR the local symmetry at an unpaired electron center is categorised as:. Cubic. If x = y = z is cubic (cubal, octahedral, tetrahedral) No anisotropy in g and A. Uniaxial (Axial).
If x = y, and z is unique. Linear rotation symmetry (at least 3 -fold). Two principal values each for g and A. For an arbitrary orientation:. Rhombic. Three unequal components for g and A For an arbitrary orientation: An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. Nitroxyl Lineshapes As the tumbling correlation time decreases, the extent of averaging of anisotropic features increases and the spectrum approaches the 3 -line signal that is characteristic of rapid tumbling.
In the motional narrowing region, the dependence of the width of an individual hyperfine line on the nuclear spin state (m. I) can be expressed as Rotation correlation times between 10 -11 and 10 -6 are detectable by ESR X-band An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. Sample Calculation 4 -OH-TEMPO (tempol) in 9: 1 glycerol: water gx = 2. 0094, gy = 2. 0059, gz = 2. 0023 Ax = 2 p 18 x 106, Ay = 2 p 22. 5 x 106, Az = 2 p 103 x 106 rad/s I(+1) = 13.
5, I(0) = 16. 4, I(-1) = 3.
52 Gauss n= 9. 2449 x 109 s-1 (arbitrary units) b = 9. 274 x 10 -21 erg/G h=6. 626 x 10 -27 erg s t= 2.
1 x 10 -9 s from B or t = 2. 3 x 10 -9 s from C The disagreement is an indication of the approximate nature of this calculation. Determination of microviscosity: (Stocks-Einstein) Extremely useful in oversaturated/overcooled disperse systems. Example: testing photographic materials An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007. Spin labeling.
Peptides and proteins Nitroxides are introduced into proteins as reporter groups to provide information about local environment, overall tumbling rate of the protein or/and segmental mobility, accessibility of the labeling site for polar/non-polar molecules, distance measurements to other spin labels, co-factors, membrane surface. Labeling of the hydroxyl group MTSL spin label is cysteine specific. SDSL = site directed spin labeling is introducing cysteines into the protein molecule by point mutations with following MTSL labeling. Cysteine mapping of the protein molecule. An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007.
Width Of Peak Electron Spin Resonance Ppt
Oxygen Accessibility Oxygen accessibility and probe mobility were measured as a function of sequence number for spin labels attached to T 4 lysozyme (T 4 L) and cellular retinol binding protein (CRBP). The correlation between the two parameters indicates that the most mobile sites are also the most oxygen accessible.
The repeat period of about 3. 6 for T 4 L is consistent with the a-helical structure of this segment of the protein. Mchaourab, C. Altenbach, and M.
Lietzow, Structure 4, 779 -783 (1996). An introduction to Electron Spin Resonance (ESR), November 7, 2007.
